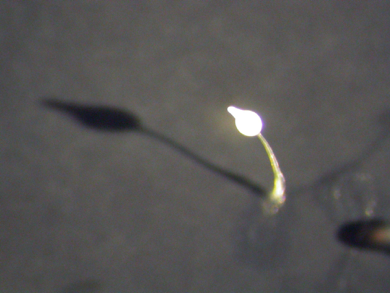
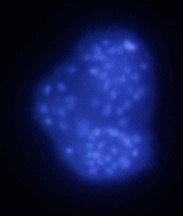
Dictyostelium (also known as social amoeba) is a primitive eukaryote, living as a single cell organism while bacteria, its source of nutrients, is present in the soil. When bacteria are consumed, starvation triggers a complex response allowing the cells to aggregate by chemotaxis and form a multicellular structure. Once the mound of cells is formed, this organism goes through a series of developmental stages based on coordinated morphogenesis and cell differentiation, to give rise to a fruiting body composed of a stalk supporting a ball of spores. Dictyostelium is easy to manipulate allowing genetic and biochemical approaches necessary to achieve complete understanding of gene function. Moreover, Dictyostelium is helping scientists to understand the molecular bases of human disease.
Much more information about this organism can be found at the Dicty-base, a central resource for the genomics and biology of Dictyostelium.